Pixar Animation Studios has been responsible for some of the most beloved animated films of all time, including Toy Story, Finding Nemo, and The Incredibles [1]. Their films have captivated audiences of all ages and have set the bar for what animated movies can achieve. But what is the secret behind Pixar’s success? A key part of the equation is the software they use.
So what software does Pixar use to create its incredible films? The answer is a combination of proprietary and industry-standard software, each tailored to the unique needs of the company’s artists and animators. Pixar’s flagship software, RenderMan, is a powerful rendering tool that is used to create the stunning visual effects that have become synonymous with Pixar’s movies.
In addition to RenderMan, Pixar also uses a variety of other software packages, including Maya, Houdini, and Nuke, to create and manipulate 3D models, simulate physics, and composite different elements of a scene.
In this article, we will take a closer look at the software that Pixar uses to create its incredible films and explore how the company’s approach to technology has enabled it to become a leader in the animation industry. We will examine the key features of Pixar’s proprietary software, as well as the industry-standard tools that are used by the company’s artists and animators. By the end of this article, you will have a greater appreciation for the technical wizardry that goes into every Pixar movie and an understanding of why the company continues to set the bar for computer-generated animation.
Pixar’s Proprietary Software
One of the key factors behind Pixar Animation Studios’ success is its proprietary software. Pixar has developed a suite of software tools that are specifically designed to meet the needs of its artists and animators.
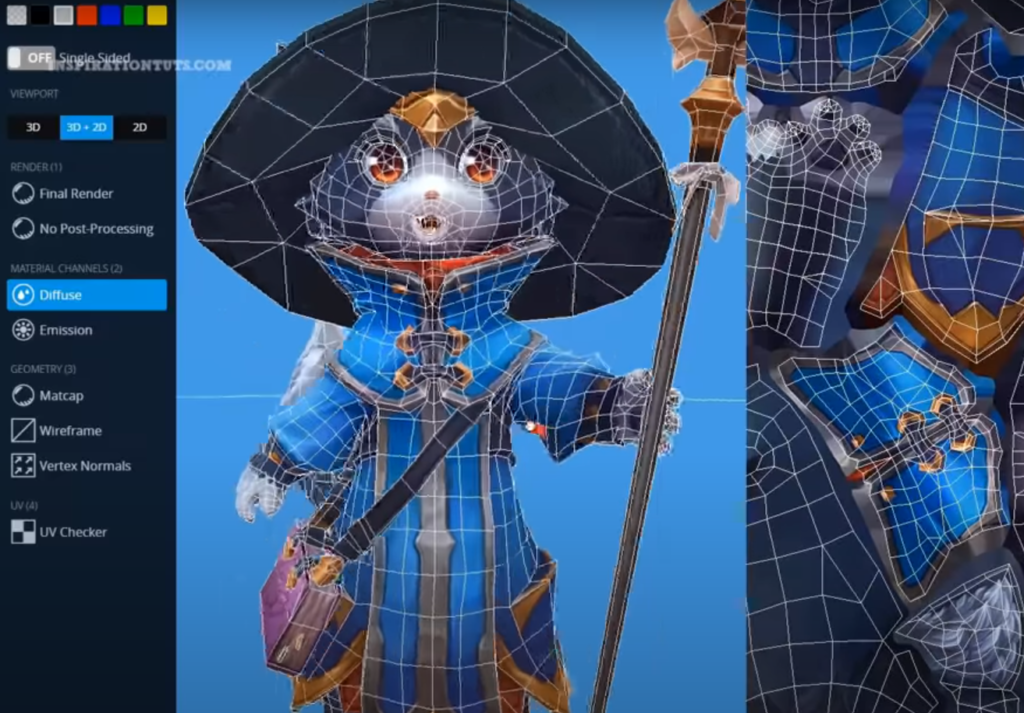

This software has enabled the company to create some of the most visually stunning and emotionally engaging animated films of all time:
1. RenderMan
The flagship software in Pixar’s suite is RenderMan. This software is a powerful rendering tool that is used to create stunning visual effects that have become synonymous with Pixar’s movies. RenderMan is a versatile and flexible tool that can be used to create a wide range of visual effects, from realistic hair and fur to complex lighting and shading.
One of the key features of RenderMan is its ability to render complex scenes quickly and efficiently. This is achieved through a process known as “ray tracing,” which involves simulating the path of light as it interacts with objects in a scene. Ray tracing can be extremely computationally intensive, but RenderMan’s advanced algorithms and optimized code make it possible to render complex scenes in a matter of hours or even minutes [2].
2. Presto
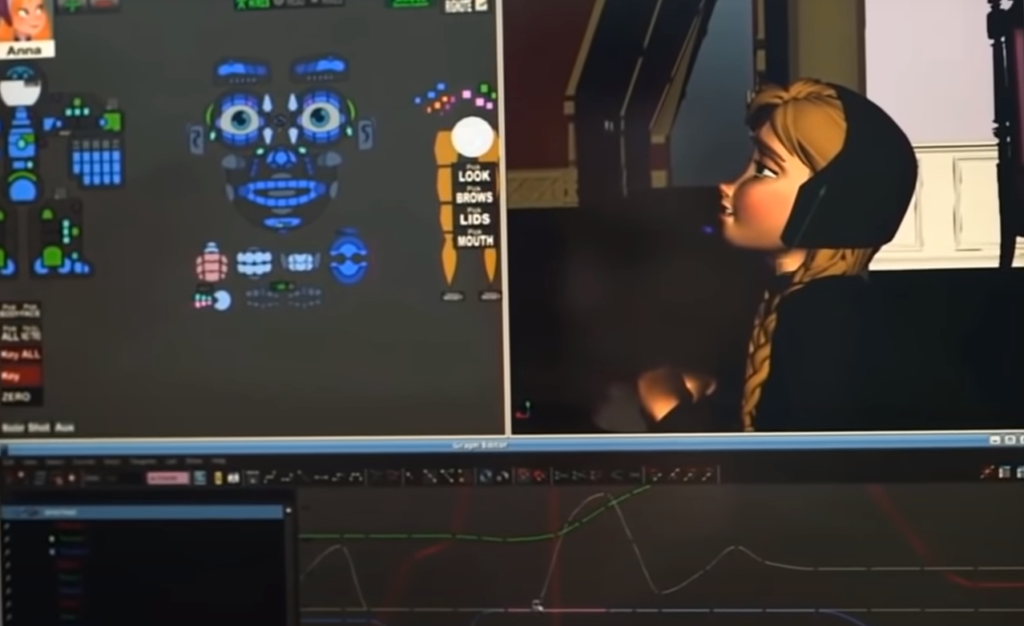
Another important piece of proprietary software in Pixar’s suite is Presto. This software is used for character animation and allows animators to create complex movements and expressions for their characters with ease. Presto is designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, allowing animators to focus on the creative aspects of their work rather than getting bogged down in technical details.
One of the unique features of Presto is its ability to provide real-time feedback to animators. This means that as an animator manipulates a character’s movements, they can see the results of their changes in real time. This allows animators to iterate quickly and experiment with different approaches to a scene, which can be invaluable in the creative process.
In addition to RenderMan and Presto, Pixar has developed a wide range of other proprietary software tools, each designed to meet the specific needs of its artists and animators. These tools include modeling and rigging software, simulation software for physics and fluids, and compositing software for combining different elements of a scene [3].
The development of proprietary software has been a key part of Pixar’s success. By creating tools that are specifically designed to meet the needs of its artists and animators, Pixar has been able to push the boundaries of what is possible with computer-generated animation. This has allowed the company to create films that are not just visually stunning, but also emotionally resonant and deeply engaging.
What Software Does Pixar Use:
1) Menv
Menv is a proprietary software tool developed by Pixar that provides a framework for managing the complexity of large-scale animation productions. Menv is used to automate and streamline many of the tasks involved in producing a computer-animated film, including managing data and workflows, scheduling tasks, and coordinating communication between different departments.
One of the key benefits of Menv is its ability to provide a unified view of the entire production process. Menv allows artists, supervisors, and producers to track the progress of a project in real-time, from the initial concept stage through to final delivery. This allows for greater collaboration and transparency throughout the production process, which can be critical in ensuring that the final product meets the high standards expected of a Pixar film.
Menv is also designed to be highly flexible and customizable, allowing different productions to tailor the software to their specific needs. This can include creating custom workflows, adding new tools and functionality, and integrating with third-party software tools.

2) Universal Scene Description (USD)
One of the key features of USD is its ability to represent complex 3D scenes as a series of “layers” that can be easily shared and manipulated. Each layer represents a different aspect of the scene, such as geometry, shading, or animation, and can be edited and versioned independently. This allows artists to work on specific aspects of a scene without having to worry about interfering with other parts of the project.
Another important feature of USD is its ability to handle complex relationships between different objects in a scene. For example, USD can be used to represent the complex interactions between a character and their environment, including their physical surroundings, other characters, and any props or objects they may interact with. This can be critical in creating convincing and realistic 3D scenes.
USD is also designed to be highly extensible and customizable, allowing different studios and artists to tailor the software to their specific needs. This can include adding custom data types, creating new tools and workflows, and integrating with other software tools.
3) OpenSubDiv
OpenSubDiv is an open-source software library developed by Pixar that is used for efficient subdivision surface evaluation. Subdivision surfaces are a key technique used in computer-generated animation to create smooth and detailed 3D surfaces. However, evaluating subdivision surfaces can be computationally intensive, particularly for complex scenes with many objects [4].
OpenSubDiv is designed to address these challenges by providing a highly optimized and parallelized subdivision surface evaluation engine. This allows for fast and efficient subdivision surface evaluation, even for very complex scenes.
One of the key benefits of OpenSubDiv is its ability to integrate with a wide range of software tools and platforms. OpenSubDiv can be used with popular 3D modeling and animation software packages such as Autodesk Maya and Blender, as well as with a range of programming languages including C++, Python, and Java. This makes it a versatile tool that can be used by animators and artists working in a range of different contexts.
Another key feature of OpenSubDiv is its ability to work with adaptive subdivisions. Adaptive subdivision is a technique used to increase the resolution of a model only where it is needed, rather than uniformly across the entire surface. This can result in significant performance gains, as well as allow for more detailed and intricate models.
OpenSubDiv also includes a range of tools for working with subdivision surfaces, including tools for converting between different representations of a model, manipulating subdivision surfaces, and visualizing subdivision surfaces.

About RenderMan Software:
Pixar RenderMan (Formerly PhotoRealistic RenderMan)
Pixar RenderMan, previously known as PhotoRealistic RenderMan, is a rendering software package that was first introduced by Pixar in 1989. RenderMan is capable of rendering extremely high-quality images with an unparalleled level of control and customization.
RenderMan uses a combination of ray tracing and global illumination to create photorealistic images. Ray tracing is a technique that simulates the path of light as it bounces around a scene, allowing for accurate reflections and refractions. Global illumination, on the other hand, simulates the indirect lighting in a scene, such as the light that bounces off walls and objects to create diffuse illumination.
Pixar RenderMan is designed to be used in conjunction with a range of 3D modeling and animation software packages, such as Maya, Houdini, and Blender. RenderMan provides a range of features and tools that allow for fine-grained control over the rendering process, including support for complex lighting scenarios, advanced texturing techniques, and sophisticated shader development [5].
One of the key benefits of RenderMan is its flexibility. RenderMan provides a range of rendering options, allowing users to choose between different rendering algorithms and techniques depending on the specific requirements of their project. This flexibility makes RenderMan an ideal choice for a wide range of projects, from small-scale indie films to large-scale Hollywood blockbusters.
RenderMan Interface Specification (RISpec)
The RenderMan Interface Specification, or RISpec for short, is a set of guidelines and specifications that define how RenderMan-compliant software should interface with RenderMan. The RISpec is designed to ensure that RenderMan can be used in conjunction with a range of different software packages and that the output of RenderMan is consistent across different platforms.
The RISpec includes a range of different components, such as a file format specification for RenderMan Scene Description (RMSD) files, a specification for the RenderMan API, and a specification for the shading language used in RenderMan shaders. These components are designed to work together to create a standardized interface that allows for seamless integration between RenderMan and other software packages.
The RISpec is constantly evolving, with new features and specifications being added over time to ensure that RenderMan remains at the cutting edge of rendering technology. The latest version of the RISpec, version 23, includes support for new features such as deep learning de-noising and ray-tracing acceleration using GPUs [6].

RenderMan Shading Language (RSL)
The RenderMan Shading Language, or RSL for short, is a programming language used to create custom shaders for use with RenderMan. Shaders are used to define how a 3D model should be rendered, specifying properties such as color, texture, and reflectivity.
One of the key benefits of RSL is its flexibility. RSL shaders can be used to create a wide range of effects, from simple diffuse shading to complex lighting scenarios involving subsurface scattering and advanced textures. RSL shaders can also be combined with other RenderMan features, such as global illumination and ray tracing, to create highly realistic images.
In addition to its flexibility, RSL is also highly optimized for use with RenderMan. RSL shaders can be compiled into highly efficient machine code that runs on the graphics processing unit (GPU) of a computer, allowing for fast and efficient rendering.
One of the strengths of RSL is its support for procedural texturing. Procedural textures are textures that are generated algorithmically, rather than being based on a pre-existing image. Procedural textures are highly customizable, allowing artists to create unique textures for each project. RSL provides a range of functions and operators for creating procedural textures, making it an ideal tool for texture artists and designers [7].
Another key feature of RSL is its support for displacement mapping. Displacement mapping is a technique used to add fine detail to 3D models by perturbing their geometry. Displacement mapping can be used to add wrinkles, creases, and other fine details to a model, making it look more realistic. RSL provides a range of functions and operators for creating displacement maps, allowing artists to create highly detailed models with a high level of control over the final result.
Professional Alternatives to Presto
One such alternative is Toon Boom Harmony. Toon Boom Harmony is a widely used animation software that offers a comprehensive set of tools for creating 2D animations. It provides a range of features, including advanced drawing tools, timeline editing, rigging, compositing, and special effects. Toon Boom Harmony also offers a variety of export options, allowing users to export their animations in a range of formats for use in different platforms and applications.
Another alternative to Presto is Autodesk Maya. Maya is a 3D animation software that offers a wide range of features for modeling, rigging, animation, and rendering. It is widely used in the film, TV, and game development industries and offers a range of advanced features, including advanced character rigging tools, physics simulations, and fluid simulations. Maya also offers a wide range of export options, making it a versatile tool for creating 3D animations for various platforms.
Blender is another alternative to Presto that has gained popularity among animators and animation studios. Blender is an open-source 3D animation software that offers a wide range of features, including modeling, rigging, animation, and rendering. It also offers a range of advanced features, including physics simulations, fluid simulations, and advanced sculpting tools. Blender has a large and active community of users and developers, making it a highly customizable and flexible tool for animation.

Cinema 4D is another professional alternative to Presto that offers a range of features for 3D animation. It is widely used in the film, TV, and game development industries and offers a range of advanced features, including advanced character rigging tools, physics simulations, and particle effects. Cinema 4D also offers a range of export options, making it a versatile tool for creating 3D animations for various platforms.
About Pixar’s Modeling Software
Pixar’s modeling software consists of several components, each of which is designed to perform specific tasks in the modeling process.
The main components of Pixar’s modeling software include:
- Modeler: The Modeler is the core component of Pixar’s modeling software. It is a tool that allows artists to create and edit 3D models using a range of advanced features, including surface modeling, subdivision surface modeling, and NURBS modeling. The Modeler also includes a range of tools for texturing, UV mapping, and rigging, allowing artists to create complex and detailed models for use in animations and visual effects;
- Sculpting tools: Pixar’s modeling software also includes a set of sculpting tools that allow artists to add fine details and textures to their 3D models. The sculpting tools include brushes, stamps, and other tools that allow artists to sculpt and paint their models with a high level of control and precision;
- Lighting and shading tools: Pixar’s modeling software also includes a range of lighting and shading tools that allow artists to create realistic lighting and shadows for their 3D models. The lighting and shading tools include a range of advanced features, including global illumination, subsurface scattering, and ambient occlusion;
- Rendering tools: Finally, Pixar’s modeling software includes a set of rendering tools that allow artists to generate high-quality renders of their 3D models. The rendering tools include a range of advanced features, including ray tracing, depth of field, motion blur, and compositing [8];

FAQ:
- Does Pixar use Windows computers?
Yes, Pixar uses Windows computers, as well as Mac computers. Pixar’s studio artists and staff use a variety of software programs, some of which are designed to run on Windows.
- Does Pixar use Autodesk?
Yes, Pixar uses Autodesk software for some of its productions, particularly in areas such as visual effects and post-production. Autodesk offers a range of software products, including Maya, which is widely used in the animation industry.
- Does Pixar use Maya?
Yes, Pixar uses Maya for its 3D modeling and animation pipeline. Maya is a popular software program used in the animation and visual effects industry and is known for its powerful 3D modeling, animation, and rendering capabilities.
- Does Pixar use Houdini?
Yes, Pixar uses Houdini for some of its productions, particularly in areas such as visual effects and simulation. Houdini is a powerful software program used in the animation and visual effects industry and is known for its procedural workflow and simulation capabilities.
- What software does Pixar use for 3D modeling and animation?
Pixar primarily uses Autodesk Maya for its 3D modeling and animation pipeline, as well as other software programs such as Pixar’s proprietary software Presto for animation.
- Did Pixar ever use third-party applications?
Yes, Pixar has used third-party applications in its productions, particularly in areas such as visual effects and post-production. Some of the third-party applications used by Pixar include Autodesk products like Maya and Arnold, as well as other software programs like Houdini and Nuke.
- What software does Pixar use for rendering?
Pixar uses its own proprietary rendering software called RenderMan for its productions. RenderMan is a powerful software program used in the animation and visual effects industry, known for its advanced rendering capabilities.
- Has Pixar ever used Blender for any projects?
To the best of my knowledge, Pixar has not used Blender for any of its productions. Pixar primarily uses Autodesk Maya and its own proprietary software for its 3D modeling and animation pipeline.
- How much does Presto cost?
Presto is Pixar’s proprietary animation software and is not available for sale to the general public. Its development and use are limited to Pixar employees and contractors.
- How much do Pixar software engineers make?
Salaries for Pixar software engineers vary depending on factors such as experience, education, and job title. According to Glassdoor, the average salary for a Pixar software engineer is around $ 187,000 per year [9].
- What 3D software does Dreamworks use?
Dreamworks primarily uses Autodesk Maya for its 3D modeling and animation pipeline, as well as other software programs such as Nuke for compositing and rendering.
- What software was used in Luca?
Luca, a 2021 animated film produced by Pixar, was primarily created using Autodesk Maya for 3D modeling and animation, Pixar’s proprietary Presto for animation, and RenderMan for rendering.
- What software did Pixar use in the 80s?
In the 1980s, Pixar primarily used software programs that were developed in-house, including Pixar’s proprietary software called RenderMan for rendering.
- What programs do Disney animators use?
Disney animators use a variety of software programs, including Autodesk Maya for 3D modeling and animation, Toon Boom for 2D animation, and other software programs for compositing and rendering.
- What computers does Pixar use?
Pixar uses a combination of Mac and Windows computers, as well as specialized hardware such as render farms and storage systems.
- What software was used in Shrek?
Shrek, a 2001 animated film produced by Dreamworks Animation, was primarily created using Autodesk Maya for 3D modeling and animation, as well as other software programs like Houdini for special effects and compositing software like Shake.
- Does Disney use Maya or Blender?
Disney primarily uses Autodesk Maya for its 3D modeling and animation pipeline, as well as other software programs like Toon Boom for 2D animation. While Blender is a popular software program, it is not widely used by Disney for its productions.
- Does Pixar use a Mac or PC?
Pixar uses both Mac and PC computers, depending on the specific needs of their artists and staff. Mac computers are often favored by artists for their design capabilities, while PC computers are often used for their processing power.
- What animation software does Studio Ghibli use?
Studio Ghibli primarily uses its own proprietary software for its productions, including software for 2D animation and compositing. However, they have also used software programs like Toon Boom for some of their productions.
- Is Maya a VFX software?
Maya is a versatile 3D modeling and animation software program used in many areas of the animation and visual effects industry. While it is often used for VFX (visual effects) work, it is not exclusively a VFX software program.
- Is Pixar animation CGI?
Yes, Pixar animation is CGI (computer-generated imagery). Pixar uses computer graphics technology to create its films, which are made up of 3D models and animations created in software programs like Maya.
- Is Maya good for CGI?
Yes, Maya is a powerful software program for CGI (computer-generated imagery). It is known for its advanced 3D modeling and animation capabilities and is widely used in the animation and visual effects industry.
- Is Pixar 2D or 3D animation?
Pixar primarily creates 3D animated films, although some of their productions have incorporated 2D animation as well. Their 3D animation is created using software programs like Autodesk Maya and RenderMan.
- Does Pixar use ray tracing?
Yes, Pixar uses ray tracing in its productions. Ray tracing is a rendering technique used to create realistic lighting and shadows in 3D graphics and is used in many areas of the animation and visual effects industry.
- Are all Pixar movies 3D?
Yes, all of Pixar’s feature films are 3D animated movies created using computer graphics technology. However, some of their productions have also incorporated elements of 2D animation as well.
- Does Maya use C++?
Yes, Maya is written in C++ programming language. C++ is a powerful programming language used in many areas of software development, including the development of 3D software programs like Maya.
- Is it hard to learn Maya?
Learning Maya can be challenging, especially for beginners. It is a complex software program with many advanced features and requires a significant amount of time and dedication to master. However, there are many resources available for learning Maya, including online tutorials and courses.
- What software does Steven Universe use?
Steven Universe, a popular animated television series, was primarily created using Toon Boom Harmony for 2D animation and compositing.
- What software is used for Rick and Morty?
Rick and Morty, a popular animated television series, is primarily created using Adobe Photoshop for character design, Toon Boom Harmony for 2D animation, and Autodesk Maya for 3D animation.

- How powerful are Pixar’s computers?
Pixar’s computers are very powerful, with specialized hardware designed to handle the complex 3D modeling, animation, and rendering processes required for their productions. Their render farms, for example, are made up of thousands of individual computers working together to render complex scenes and sequences.
- Can Blender replace Maya?
While Blender is a powerful software program with many advanced features, it may not be able to fully replace Maya for all purposes. Maya is a widely used software program in the animation and visual effects industry and is known for its advanced 3D modeling and animation capabilities. However, Blender can be a good alternative for some users who are looking for a free and open-source software program with similar capabilities.
- Does Marvel studios use Blender?
Marvel Studios primarily uses Autodesk Maya for its 3D modeling and animation pipeline, as well as other software programs like Houdini for special effects and compositing software like Nuke. While Blender is a popular software program, it is not widely used by Marvel Studios for its productions.
Useful Video: What Software Does Pixar Use?
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Presto_(animation_software)
- https://www.pixar.com/renderman
- https://vertexmode.com/what-software-does-pixar-use/
- https://inspirationtuts.com/what-software-does-pixar-use/
- https://www.blenderbasecamp.com/home/what-software-does-pixar-use/
- https://thisanswer.com/what-3d-animation-software-does-pixar-use-2/
- https://nixologic.com/what-software-does-pixar-use/
- https://www.hillstone-software.com/what-animation-software-does-pixar-use/
- https://www.glassdoor.com/Salary/Pixar-Animation-Studios-Software-Engineer-Salaries-E5118_D_KO24,41.htm









Leave a Review